Privacy remains one of the main unresolved problems of blockchains. The complete transparency of networks limits their functionality, making many use cases impossible. Arcium offers an alternative: data processing without revealing it. The project positions itself as a high-performance “encrypted supercomputer” combining cryptography and multi-party computation.
In this review, we examine how Arcium works and whether the project can set fundamentally new standards for on-chain privacy.
The problem of data protection in decentralized networks and possible solutions
One of the fundamental principles of public blockchains (with the exception of confidential networks like Monero) is transparency, which allows every user to view the transactions of any wallet at any time. However, this openness is often an obstacle to maintaining the confidentiality of personal and corporate data, which is widespread in traditional finance.
In situations where institutional investors, venture funds, and companies seek to protect the details of their transactions, the complete publicity of the blockchain turns from an advantage into a disadvantage, complicating the adoption of the technology. To solve this problem, a number of solutions have emerged that ensure privacy in individual processes and aspects.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) — allow you to confirm the truth of a statement, for example, the availability of sufficient funds for a transaction, without revealing the source data.
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) — allows you to process encrypted data, but requires significant computing power.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) — these are isolated and secure execution environments within hardware devices in which data can be securely processed.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) — provides the ability for multiple participants to jointly perform computations without revealing their data to each other, making this method the most versatile for ensuring privacy.
Each of these technologies protects individual data at different stages of user interaction with the blockchain or a specific protocol, but does not provide end-to-end confidentiality across the entire network. According to Arcium developers, this “privacy 1.0” is characterized by fragmentation and focus on protecting the “private” state of an individual user, rather than the public state of the blockchain.
To improve the efficiency of data protection in decentralized networks, Arcium offers the concept of “privacy 2.0.” Using MPC technologies and cryptography, the project developers are creating an infrastructure in which privacy is a “default” property of the blockchain, and operations with encrypted data are performed faster and more efficiently than with existing solutions.
What is Arcium
Arcium is positioned as a decentralized encrypted computing network or “supercomputer” that allows developers and users to work with data without revealing it.
In most existing systems, encryption is applied only when storing (at rest) and transferring (in transit) data. This also applies to the blockchain, where, for example, ZKP allows you to protect transmitted information, and cryptography protects stored information. Arcium adds another layer of protection — during calculations (in use).
This means that the information remains encrypted at all stages of processing, that is, theft, leakage, or misuse is technically impossible. This approach makes it possible to safely use confidential information in DeFi, AI platforms, and other areas where data protection plays a key role.
Arcium network architecture
Arcium is a decentralized computing network designed for confidential data processing. It combines several key components that ensure the security, scalability, and reliability of the system. Let’s analyze each element of the Arcium architecture and its role in the system.
arxOS
arxOS is a software shell that manages all processes in the Arcium network, including:
- coordination of node operations — the system automatically distributes computations between nodes, selecting the most suitable ones in terms of power and reliability;
- performance monitoring — arxOS tracks the status of each node and cluster, preventing failures and overloads;
- security assurance — the operating system implements fault tolerance mechanisms and prevents unauthorized changes in computing processes.
At the same time, arxOS is not centralized and functions autonomously on each network node, which eliminates the possibility of a single point of failure.ет автономно на каждом узле сети, что исключает возможность единой точки отказа.
Arx Nodes
Arx Nodes are independent servers (nodes) that perform computations in the Arcium network. They accept tasks, perform them in encrypted form, and transmit the result without having access to the source data. Each node consists of two key components:
- hardware — the node must meet the minimum requirements for computing power, since complex cryptographic operations require resources. Operators independently declare technical specifications, and slashing is applied to those who overstate their indicators and cannot handle the load;
- software — the operation of the nodes is coordinated by the aforementioned arxOS, and the calculations themselves take place within special MXE environments (more on them below).
To ensure data protection, nodes use specialized solutions including cryptography, MPC protocols, and TEE.спользуют специализированные решения включая криптографию, MPC-протоколы и TEE.
Clusters
Arx Nodes are combined into clusters, within which they jointly perform multi-party computations. If one node fails or works slowly, the system redistributes its tasks among the others.
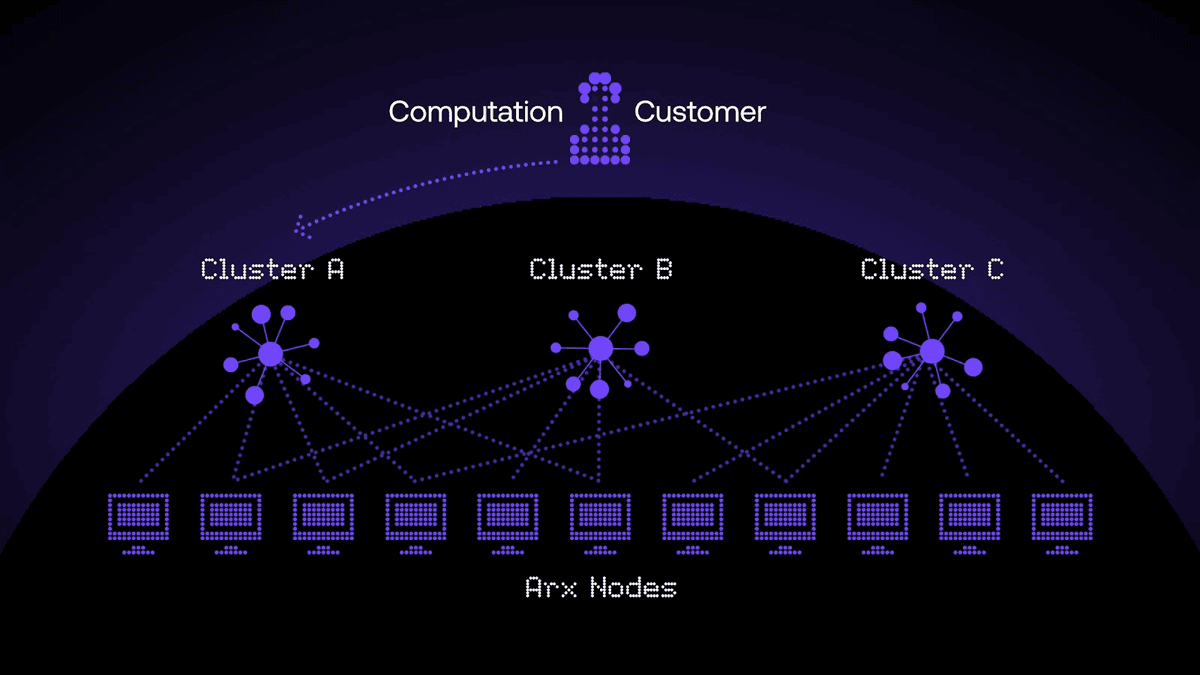
Clusters can operate according to several trust models:
- Honest but Curious — all participants behave in accordance with the protocol rules, but at the same time try to collect as much data as possible. The information itself remains encrypted in this case.
- Honest Majority — the system maintains data confidentiality and integrity if at least half of the cluster nodes behave honestly.
- Dishonest Majority — computations remain protected as long as at least one cluster node follows the protocol rules.
Clusters allow Arcium to maintain flexibility, reliability, and scalability by efficiently distributing tasks between nodes.
MXE (Multi-Party eXecution Environments)
MXE are virtual environments in which computations take place. They allow performing mathematical operations on encrypted data without decrypting it, ensuring confidentiality at all stages of processing. Each MXE is an isolated execution environment in which input data and processing results remain encrypted. There are two main types of MXE:
- Disposable — created to perform a specific task and destroyed immediately after completion, leaving no data traces.
- Persistent — remain active and can continuously process new input data. This is useful for long-term computations, such as training AI models or executing smart contracts.
MXE are flexible and customizable, allowing developers to choose the level of security, data encryption algorithms, and data storage policies.зработчикам выбирать уровень безопасности, алгоритмы шифрования информации и политику хранения данных.

The operation of this entire system is based on the aforementioned multi-party computations. They allow multiple nodes to jointly perform an operation without revealing the source data, since each node processes only its part of the information. At the end of processing, the results are combined into a common response that can only be decrypted by the recipient.
At the same time, Arcium uses two MPC protocols:
- Cerberus — guarantees maximum protection, maintaining confidentiality even in the event of attacks from most nodes.
- Manticore — offers higher computation speed, but requires a more trusted environment.
The choice between these protocols allows users and developers to customize security for specific scenarios.
Integration with the blockchain
Arcium was initially developed as a blockchain-agnostic solution, but in the first stage of development, the project chose Solana as its base ecosystem. This is due to the high throughput and fast transactions of the network, which are necessary for managing computational processes.
The blockchain provides three key functions for Arcium:
- Node management. Solana acts as a coordination layer that provides node registration and configuration, monitors their computing power, and records performance and reliability.
- Computation orchestration. Task distribution in Arcium takes place in Solana, in particular, the network collects tasks from users and applications, as well as their entry into the mempool, cluster formation of nodes, and verification of the correctness of completed calculations.
- Network economics. Solana also manages Arcium’s incentive mechanisms, including node rewards for completed calculations, staking for admission to calculations, and penalties for dishonest node operation.
However, although Solana is the first integrated blockchain, the project will be able to work in other ecosystems in the future. In particular, Arx Nodes will be able to perform tasks in different networks, choosing the optimal infrastructure based on load, transaction cost, and speed, and Arcium will provide synchronization of results.имальную инфраструктуру с учетом нагрузки, стоимости транзакций и скорости работы, а Arcium обеспечит синхронизацию результатов.
Capabilities and use cases of Arcium
The ability to work with encrypted data without revealing it allows expanding the scope of blockchain use, as well as increasing the diversity and functionality of decentralized products and applications.
Thus, Arcium provides developers with a platform to create decentralized applications where security and privacy are implemented “by default.” For example:
- Confidential DeFi Platforms: Developers can create financial services where users interact with contracts without revealing personal data or their trading strategies. This makes possible, for example, anonymous liquidity or untraceable transactions.
- Secure AI Training: Companies can use confidential data sets to train AI models without violating regulatory norms and without exposing personal information to the risk of theft or leakage.
- Anonymous Auctions and Marketplaces: Arcium allows creating trading platforms where users place bids or make deals without revealing personal data, which is especially important for the B2B segment.
A more applied example, not directly related to the blockchain, is the use of private algorithms to match partners in dating services or professional networks without disclosing their information.
For ordinary users, Arcium provides complete control over their data, allowing them to interact with the blockchain without the threat of information disclosure. This provides new opportunities:
- Secure Data Exchange and Storage: Users can control access to their information, as well as transmit and analyze it without actual disclosure—this is relevant for medical research, corporate reports, and personal files.
- Protected Trading: Arcium allows creating so-called “Dark Pools” in which large investors can conduct transactions without the risk of front-running and market manipulation.
- Private Voting and Prediction Markets: DAOs and decentralized prediction markets can implement anonymous voting in which results remain hidden until the final count.
Support and partners
Project funding and development
According to CryptoRank, Arcium has managed to raise $9 million in two funding rounds, the latest of which took place in May 2024. Among the investors are leading venture funds and key industry figures, including Coinbase Ventures, Jump Crypto, Greenfield Capital, NGC Ventures, as well as Solana co-founder Anatoly Yakovenko and Monad co-founder Keon Hon.
Notably, the repeat investment took place a year and a half after the first. This suggests that the team has been actively developing the project for a long time, and investors have maintained their interest.
One of the important stages in the project’s development was the acquisition of Inpher in early 2024. Inpher is a leader in the Web2 segment in the field of encrypted computing, previously receiving support from giants such as JPMorgan and Amazon. This deal strengthened Arcium’s position in the field of confidential data processing, adding experienced specialists to the team and expanding the technical base.
In addition, the acquisition of Inpher gave Arcium access to an optimized technology stack for developing confidential AI solutions. This made it possible to create a platform on which machine learning models can be trained on encrypted data.
In March 2024, Arcium was included in the NVIDIA Inception program, which helps innovative startups develop AI-based products. The scope of confidential AI solutions created within this partnership covers healthcare, finance, scientific research, and defense. In addition, participation in the program provides Arcium with access to NVIDIA’s advanced computing resources.
Additionally, it is worth noting that interest in the project among users is high — more than 40,000 applications were submitted to participate in the Arcium closed testnet, and almost 400,000 NFTs were generated as part of the network’s functionality testing. At the time of writing, the platform is in the final phase of closed testing, after which it will be ready for public launch.
Token and tokenomics
At the time of writing, there is no official information about the Arcium token, tokenomics, and distribution terms. However, there is a high probability that the platform will receive its own token in the future, as the developers have already launched activities related to a potential airdrop, and the network’s operating model provides for staking.
Thus, to activate an Arx node, it will be necessary to lock a certain number of tokens, which will allow operators to participate in task distribution. Delegators, in turn, will be able to transfer their assets to the latter, receiving a portion of the rewards for calculations.
Although the details have not yet been disclosed, it can be assumed that the Arcium token will perform several basic functions:
- payment for computing power — users will probably use the token to initiate private calculations on the platform;
- node rewards — node operators, performing calculations, will receive tokens for their work;
- participation in network governance — the token can be used for voting and making decisions in the Arcium ecosystem.
Users are advised to follow the project’s announcements on the website and social networks to receive the latest information about the token, airdrop, or Arcium’s public sales.ьных сетях, чтобы получать свежую информацию о токене, аирдропе, или публичных продажах Arcium
Conclusions
As blockchain spreads, decentralized networks face a problem: transparency is useful, but hinders privacy. Previously created solutions partially eliminate this obstacle, but remain either highly specialized or too resource-intensive.
Arcium offers a different approach—confidentiality as a fundamental property of the network. This is not just the protection of individual transactions, but a full-fledged infrastructure for encrypted computing, in demand in DeFi, the corporate sector, AI, and when working with user data.
Even before the mainnet launch, the project attracted $9 million in investments, acquired Inpher, a company specializing in confidential computing, and entered NVIDIA Inception, which confirms the long-term strategy of the developers. Unlike many other Web3 projects, Arcium is building a technological base before launching the token, and not vice versa.
However, the project faces challenges: competition with other solutions like Aleo and Aztec, regulatory risks, and the need to integrate into the Web3 ecosystem. If Arcium overcomes these barriers, it can set a new standard for confidential computing in the blockchain.
